Difference between Array and Linked List
Linked List vs. Array
Array is a datatype which is widely implemented as a default type, in almost all the modern programming languages, and is used to store data of similar type.
But there are many usecases, like the one where we don't know the quantity of data to be stored, for which advanced data structures are required, and one such data structure is linked list.
Let's understand how array is different from Linked list.
| ARRAY | LINKED LIST |
|---|---|
| Array is a collection of elements of similar data type. | Linked List is an ordered collection of elements of same type, which are connected to each other using pointers. |
Array supports Random Access, which means elements can be accessed directly using their index, like
arr[0] for 1st element, arr[6] for 7th element etc.
Hence, accessing elements in an array is fast with a constant time complexity of
O(1). |
Linked List supports Sequential Access, which means to access any element/node in a linked list, we have to sequentially traverse the complete linked list, upto that element.
To access nth element of a linked list, time complexity is
O(n). |
In an array, elements are stored in contiguous memory location or consecutive manner in the memory.
|
In a linked list, new elements can be stored anywhere in the memory.
Address of the memory location allocated to the new element is stored in the previous node of linked list, hence formaing a link between the two nodes/elements.
|
| In array, Insertion and Deletionoperation takes more time, as the memory locations are consecutive and fixed. |
In case of linked list, a new element is stored at the first free and available memory location, with only a single overhead step of storing the address of memory location in the previous node of linked list.
Insertion and Deletion operations are fast in linked list.
|
| Memory is allocated as soon as the array is declared, at compile time. It's also known as Static Memory Allocation. | Memory is allocated at runtime, as and when a new node is added. It's also known as Dynamic Memory Allocation. |
| In array, each element is independent and can be accessed using it's index value. | In case of a linked list, each node/element points to the next, previous, or maybe both nodes. |
| Array can single dimensional, two dimensional or multidimensional | Linked list can be Linear(Singly), Doubly or Circularlinked list. |
| Size of the array must be specified at time of array decalaration. | Size of a Linked list is variable. It grows at runtime, as more nodes are added to it. |
| Array gets memory allocated in the Stacksection. | Whereas, linked list gets memory allocated in Heapsection. |
Below we have a pictorial representation showing how consecutive memory locations are allocated for array, while in case of linked list random memory locations are assigned to nodes, but each node is connected to its next node using pointer.
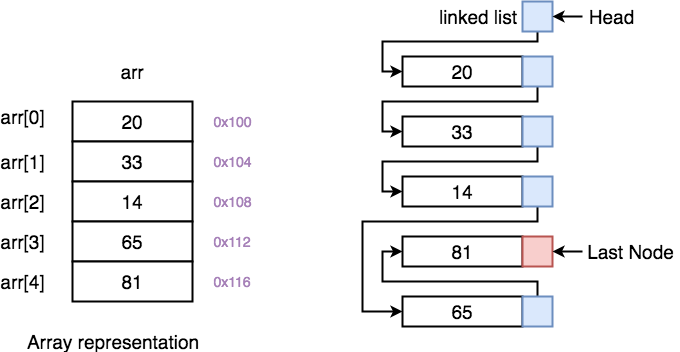
On the left, we have Array and on the right, we have Linked List.
Comments
Post a Comment
Thanks for comment. We will get back to you soon...